Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- michigan university deep learning for computer vision
- 분석 툴
- 브라이틱스 AI
- pymysql
- 파이썬 SQL 연동
- 삼성 SDS 서포터즈
- Deep Learning for Computer Vision
- 서포터즈 촬영
- Python
- 삼성 SDS
- Brightics 서포터즈
- Brightics studio
- 비전공자를 위한 데이터 분석
- Brigthics Studio
- 브라이틱스 프로젝트
- 브라이틱스 서포터즈
- paper review
- 데이터 분석
- 파이썬 내장 그래프
- Activation Function
- 브라이틱스 스태킹
- Random Forest
- 머신러닝
- 딥러닝
- Brightics AI
- 데이터 분석 플랫폼
- Brightics EDA
- 범주형 변수 처리
- 브라이틱스 분석
- 검증 평가 지표
Archives
- Today
- Total
하마가 분석하마
[python] pymysql을 사용한 sql 연동2 본문

python과 mysql 연동
with 문을 사용해서 확인
- 파일을 열고 사용한 뒤, 반납의 과정
- 데이터베이스 세션을 얻어 사용했다면 다른 프로세스를 위해 반납
- 자동으로 마지막에 close()를 해줌
0. commit이란?
- commit 명령어는 모든 작업을 정상적으로 처리하겠다고 하는 명령어이다.
- 쿼리문의 내용을 DB에 반영하기 위해, 처리된 내용을 모두 영구 저장한다.
- commit을 수행하면, 하나의 트랜젝션 과정이 종료된다.
- auto commit을 설정하여 자동으로 바뀌게 설정할 수 있는데 commit을 하게 되면 데이터 복구가 어렵기에 주의해야 한다.
1. try | finally + with
- finally를 사용하여 마지막에 DB 연결을 닫아줘야 함
- 단순하게 데이터를 불러오는 경우에는 commit()을 하지 않아도 된다.
- sql의 DML 언어를 사용할 때만 commit을 하면 된다.
### 1번 test
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port,charset='utf8')
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from exam_result"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
# commit을 이용하여 데이터를 확정지어야 한다.
result.commit()
for i in result:
print(i)
finally:
# close()를 사용해서 DB 연결을 닫는다.
connection.close()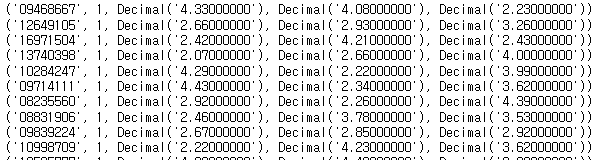
2. 한글 출력
### 2번 test
# 한글이 정상적으로 출력되지 않을 때
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port)#,charset='utf8')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from major"
# 데이터베이스 정의 시 charset='utf8'로 하였어도 한글이 제대로 안 뜰 수가 있다.
# 이럴 경우 .execute("set names utf8") 사용
cursor.execute("set names utf8")
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
connection.commit()
for i in result:
print(i)
3. insert문의 사용
- table에 insert into로 데이터 추가
## 3번 테스트
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8')
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "Insert into major values (%s, %s, %s)"
# 포맷팅 사용
cursor.execute(sql, (107, "통계학과", '손흥민'))
cursor.execute(sql, (108, "경영학과", '올라프'))
# execute() 만으로는 실행이 일어나지 않는다.테이블의 변화를 지시하는 함수
# commit()을 사용해야 변화가 일어난다.
connection.commit()
finally:
connection.close()
추가 되었는지 결과 확인
## 추가 되었는지 확인
# 손흥민과 올라프 관측치가 추가되었음을 알 수 있다.
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8')
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from major"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for i in result:
print(i)
finally:
connection.close()
4. update문의 사용
## 손흥민의 학과를 토트넘으로 변경
# connection을 다시 설정해주는 이유는 앞에서 close()를 했기 때문
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8')
# try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "update major set major_nm = %s where professor_nm = %s"
cursor.execute(sql, ('토트넘', '손흥민'))
# update더 insert와 마찬가지로 commit을 해줘야 한다.
connection.commit()
# finally:
# connection.close()## 추가 되었는지 확인 -> 알맞게 바뀜
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from major"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for i in result:
print(i)
finally:
# connection을 1번 더 불러오지 않기 위해 updqte문에서 try, finally를 제외함
connection.close()
5. delete 문의 사용
- delete 문으로 관측값 제거 후 바로 확인
## connection 설정
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8')
try:
### 관측값 제거
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql="delete from major where professor_nm=%s"
cursor.execute(sql, '올라프')
# cursor 객체가 아닌 connection에 commit 해야함
connection.commit()
### 결과 확인
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = 'select major_cd, major_nm, professor_nm from major'
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for i in result:
print(i)
finally:
connection.close()
## 올라프 관측치가 잘 사라졌음을 알 수 있음
6. 튜플 변수를 사용한 update
## connection close 여부를 확인 후 진행
# 위에서 close를 하지 않았기에 그대로 진행
try:
professor_name = '손흥민'
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = 'update major set major_nm=%s where professor_nm=%s'
cursor.execute(sql, ('맨시티', professor_name))
connection.commit()
# connection.commit()
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from major"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
# for 문을 with문 안에 써도 된다.
for i in result:
print(i)
finally:
connection.close()
7. 관측치 한 번에 여러 개 추가
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
data = (
('108', '포르투','헐크'),
('109', 'psg', '네이마르')
)
sql = ("insert into major values (%s, %s, %s)")
# execute문으로 여러 개를 동시에 추가하는 것은 불가능
# executemany를 사용해야 함
cursor.executemany(sql, (data))
connection.commit()
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = ("select * from major")
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for i in result:
print(i)
8. Dictionary Cursor를 이용한 데이터 조회
- 데이터 조회
connection = pymysql.connect(host=host, user=username, passwd=password, db=database, port=port, charset='utf8', cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
try:
with connection.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as cursor:
sql = """select *
from major"""
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for i in result:
print(i['major_cd'])
finally:
connection.close()
'python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python] try | except | else | finally (0) | 2022.01.16 |
|---|---|
| [python] pymysql을 사용한 sql 연동1 (0) | 2021.12.23 |
| [python] 내장 그래프 3 (histogram, kernel density, pie) (0) | 2021.07.29 |
| [python] 내장 그래프 2 (boxplot, barplot) (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| [python] 내장 그래프 1 (line, scatter) (0) | 2021.07.22 |




